Understanding Collateralized Loan Obligations (CLOs)
Collateralized Loan Obligations (CLOs) are complex financial instruments that play a significant role in the global financial market. As structured investment vehicles, CLOs pool together various loans and debt securities to create diversified portfolios for investors. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of CLOs, exploring their structure, creation process, investor profiles, risks, regulation, and market trends.
Structure of CLOs
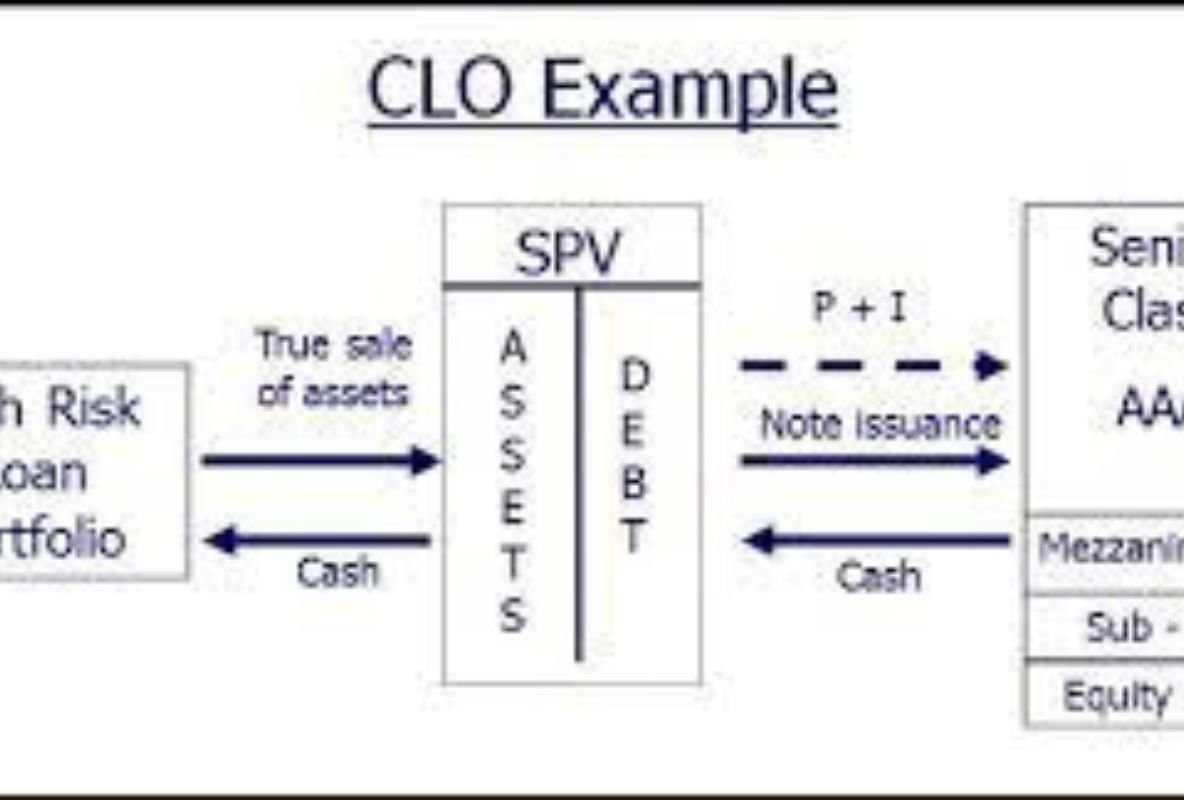
CLOs are structured investment vehicles that contain a diverse pool of loans, typically corporate loans, and debt securities. These loans are bundled together and divided into different tranches based on their risk profiles and expected returns. The structure of CLOs involves the issuance of securities backed by the cash flows generated from the underlying loan portfolio.
Types of Collateral in CLOs
The collateral assets within CLOs can include a variety of debt instruments, such as leveraged loans, corporate bonds, and structured finance products. Collateral managers play a crucial role in selecting and managing the assets within the CLO portfolio, aiming to achieve optimal risk-adjusted returns for investors while maintaining diversification and liquidity.

Creation Process of CLOs
The creation process of CLOs involves several key steps, including the acquisition of underlying loans, structuring the CLO transaction, and issuing securities to investors. Special purpose vehicles (SPVs) are used to isolate the CLO assets from the sponsoring financial institution’s balance sheet, providing investors with a degree of protection in the event of default.
Investors in CLOs
Investors in CLOs include a diverse range of institutions and individuals seeking exposure to fixed income securities with varying risk and return profiles. Different tranches of CLO securities appeal to investors with different risk tolerances, offering opportunities for enhanced yield potential in exchange for assuming higher levels of credit risk.
Risks Associated with CLOs
While CLOs offer potential benefits in terms of diversification and yield enhancement, they also carry inherent risks. Credit risk, market risk, and liquidity risk are among the primary concerns for investors in CLO securities, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty or financial market volatility.
Regulation and Oversight of CLOs
Regulatory oversight of CLOs varies by jurisdiction, with regulatory bodies imposing guidelines and requirements to promote transparency, stability, and investor protection in the CLO market. Since the global financial crisis of 2008, regulatory scrutiny of CLOs has intensified, leading to reforms aimed at mitigating systemic risks and enhancing market resilience.
Performance and Market Trends
Historically, CLOs have demonstrated resilience and performed well under diverse market conditions. However, shifts in investor sentiment, changes in credit quality, and macroeconomic factors can influence the performance and market dynamics of CLOs. Emerging trends in the CLO market include technological innovation, evolving investor preferences, and regulatory developments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Collateralized Loan Obligations (CLOs) play a vital role in the global financial ecosystem, offering investors access to diversified portfolios of loans and debt securities. While CLOs present opportunities for enhanced returns, investors must carefully assess the associated risks and remain vigilant amidst evolving market conditions.