The US National Debt, an ever-present figure in economic discussions, is more than just a numerical value. It represents a complex interplay of economic policies, government spending, and global dynamics. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the US National Debt, exploring its definition, historical context, current scenario, and the implications it holds for the nation’s economic future.
Defining the US National Debt
What is the US National Debt?
The US National Debt is the total amount of money that the federal government owes to external creditors, domestic lenders, and various government accounts. It encompasses the cumulative effect of borrowing to fund budget deficits and cover government expenses that exceed revenue.
Components of the US National Debt
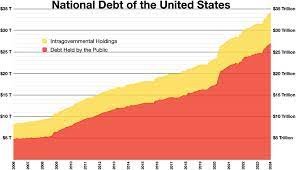
Breaking down the components of the US National Debt reveals a comprehensive picture. It includes public debt held by individuals, corporations, and foreign governments, as well as intragovernmental holdings representing money the government owes to itself.
Historical Perspectives on US National Debt
Foundations and Early Years
The roots of the US National Debt trace back to its early days. The need for funds to establish the fledgling nation and support the Revolutionary War led to the issuance of government bonds, marking the inception of the debt.
Major Moments in National Debt History
Post-WWII Era
The end of World War II marked a notable increase in the US National Debt, reflecting the massive expenditures associated with the conflict. However, subsequent decades saw efforts to manage and reduce the debt burden.
Contemporary Challenges
Recent years have witnessed a resurgence in the growth of the US National Debt. Economic crises, wars, and significant policy initiatives have contributed to the escalating figures, bringing the nation face to face with critical fiscal challenges.
Current Scenario: Unraveling the Numbers
Figures and Statistics
As of the latest available data, the US National Debt has reached staggering levels, surpassing trillions of dollars. Analyzing these figures unveils the complexity of the nation’s financial obligations and the scale of borrowing required to sustain government operations.
Factors Contributing to the Debt Increase
Government Spending
One of the primary drivers of the escalating US National Debt is government spending. From infrastructure projects to social programs, each expenditure contributes to the growing financial burden.
Taxation Policies
The balance between revenue generation and government spending is intricately linked to taxation policies. The adequacy of tax collections impacts the need for borrowing to sustain budgetary requirements.
Economic Conditions
The overall state of the US economy, influenced by factors such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation, plays a significant role in shaping the trajectory of the National Debt.
The Pros and Cons of the US National Debt
Advantages
Economic Stimulus
Strategic borrowing can serve as an economic stimulus, especially during downturns. By injecting funds into the economy, the government can spur growth and job creation.
Infrastructure and Social Investments
National debt allows the government to finance critical infrastructure projects and social programs, contributing to long-term development and societal well-being.
Disadvantages
Burden on Future Generations
A persistent concern associated with high national debt is the burden it places on future generations. As debt accumulates, the responsibility of repayment falls on the shoulders of succeeding citizens.
Risk of Fiscal Instability
Excessive national debt levels pose a risk to fiscal stability. High-interest payments, potential credit rating downgrades, and limited fiscal maneuverability are among the challenges that can arise.
Government Policies and Strategies for Debt Management
Debt Reduction Initiatives
Governments employ various strategies to manage and reduce the US National Debt. These may include implementing policies to achieve budget surpluses, reducing unnecessary expenditures, and exploring avenues for increased revenue.
Fiscal Policies and Budgetary Discipline
Adopting sound fiscal policies and maintaining budgetary discipline are crucial components of effective debt management. Striking a balance between revenue collection and government spending is essential to curb the growth of the National Debt.
Global Perspectives: How the US National Debt Impacts the World
Economic Interconnectedness
The US National Debt’s repercussions extend beyond national borders. Given the global interconnectedness of economies, the fiscal health of the United States has implications for international markets, trade relationships, and overall economic stability.
Dollar Dominance and Reserve Currency Status
The US dollar’s status as the world’s primary reserve currency is closely linked to the stability of the US economy. High levels of national debt could potentially challenge this dominance and reshape the global economic landscape.

Addressing Concerns and Debunking Myths
Common Misconceptions
Myth: National Debt is Always Harmful
Contrary to popular belief, not all national debt is inherently harmful. Responsible borrowing and strategic investments can contribute to economic growth.
Myth: The US Can Never Repay its Debt
The goal is not necessarily complete repayment but managing the debt effectively to ensure sustainability. Responsible fiscal policies can alleviate concerns about the US’s ability to service its debt.
Future Outlook: Challenges and Opportunities
Economic Forecasting
Examining economic forecasts provides insights into the trajectory of the US National Debt. Proactive measures and policy adjustments may be necessary to navigate potential challenges on the horizon.
Balancing Act for Sustainable Growth
Striking a delicate balance between fostering economic growth and managing the National Debt is crucial for the nation’s future. Implementing policies that support development without jeopardizing fiscal stability remains a formidable challenge.
Conclusion
The US National Debt, a dynamic and ever-evolving entity, is emblematic of the intricate relationship between government finance and economic prosperity. As the nation grapples with the challenges posed by the escalating debt figures, informed discussions, responsible policies, and strategic fiscal management will play pivotal roles in determining the trajectory of the United States’ economic future.
FAQs
- How is the US National Debt calculated?
- The US National Debt is calculated by summing up the total amount of money that the federal government owes to external creditors, domestic lenders, and various government accounts.
- What are the major factors contributing to the increase in the US National Debt?
- The primary factors include government spending on various projects and programs, taxation policies, and the overall economic conditions influencing revenue and expenditures.
- Can the US ever fully repay its National Debt?
- The goal is not necessarily complete repayment but effective management to ensure sustainability. Responsible fiscal policies play a crucial role in servicing and managing the debt effectively.
- How does the US National Debt impact the global economy?
- The US National Debt’s repercussions extend globally, influencing international markets, trade relationships, and the overall economic stability due to the interconnectedness of economies.
- What are the advantages of the US National Debt?
- Advantages include its potential role as an economic stimulus during downturns and the ability to finance critical infrastructure projects and social programs for long-term development.
